Numerical simulation of the influence of coal mining subsidence cracks on the moisture migration law in the vadose zone
-
摘要:
采煤塌陷裂缝,影响包气带水分运移规律,诱发矿区生态地质环境问题。当前研究集中于塌陷裂缝对包气带含水率影响,往往忽略塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移方向及其速度的影响。为此,综合考虑裂缝宽度、裂缝密度和土壤质地类型,基于HYDRUS 2D建立采煤塌陷区包气带水分运移数值模型,研究采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移规律。结果表明:单一裂缝时,含水率差距与裂缝宽度呈正相关关系;土壤水分运移方向向裂缝处偏转,同一土壤深度越靠近裂缝的区域偏转角度越大,最大偏转角度和发生运移方向变化的区域大小随裂缝宽度变大而变大; 裂缝边缘与远离裂缝区域的平均水分运移速度差值随裂缝宽度变大而变大; 裂缝密度增高时,同一土壤深度含水率会随之降低,裂缝之间区域的最大偏转角度与发生偏转的区域变小; 采煤塌陷裂缝影响下壤土的含水率高于风沙土、水分运移速度低于风沙土,但土壤质地类型不影响水分运移方向。
Abstract:Coal mining subsidence cracks affect the moisture migration law in the vadose zone, inducing ecological and geological environmental issues in mining areas. Current research focuses on the influence of subsidence cracks on the moisture content in the vadose zone, often overlooking the impact of subsidence cracks on the direction and speed of the moisture migration. Therefore, considering the width of cracks, crack density, and soil texture types, a numerical model of moisture migration in the vadose zone of coal mining subsidence areas was established based on HYDRUS 2D, to study the law of moisture migration under the influence of coal mining subsidence cracks. The results show that when there is a single crack, the difference in moisture content is positively correlated with the crack width. The direction of soil moisture movement is diverted towards the crack, and the closer the region to the crack at the same soil depth, the greater the diversion angle. The maximum diversion angle and the size of the region where the direction of movement changes increase with the widening of the crack. The difference in average moisture movement velocity between the crack edge and the region far from the crack increases with the crack width. With an increase in crack density, the moisture content at the same soil depth decreases, and the maximum diversion angle between regions between cracks and the occurrence of diversion decreases. Under the influence of coal miming subsidece cracks, the molsture content of loam is higher than that of aeolian sandy soil, and the moisture migration speed is lower than that of aeolian sandy soil, but the soil texture type does not affect the direction of moisture migration.
-
随着中东部煤炭资源的枯竭,我国煤炭资源开发中心已转移至西北部地区。西北大部分区域属于干旱半干旱区域,生态地质环境脆弱、水资源匮乏。包气带水分是该区域植被生态重要水资源。煤炭资源大规模开采造成地表塌陷裂缝,影响包气带水分运移规律,易诱发植被枯萎、沙漠化、滑坡、坍塌、潜水位下降等生态地质环境问题 [ 1- 2] 。因此,阐明塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移的影响规律,对实现矿区生态地质环境保护和绿色矿山建设具有重要意义。
当前针对采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移规律影响研究,取得了丰硕成果。琚成远 [ 3] 、毕银丽 [ 4] 、杜国强 [ 5] 等通过实地测量、数值模拟分析、室内模拟实验等方式进行研究后认为,采煤塌陷裂缝使土壤的含水率降低,且土壤含水率的降低受到裂缝宽度和区域与裂缝之间距离的影响;张延旭等 [ 6] 通过实地测量毛乌素沙漠的土壤含水率发现除了裂缝宽度与裂缝距离外,塌陷裂缝的密度也会对土壤含水率产生影响,裂缝的密度与土壤含水率呈负相关关系;陈建平等 [ 7] 通过室内模拟实验进一步发现塌陷裂缝不仅会对土壤含水率产生影响,还会使土壤中的水分运移由原本的垂向一维扩散变成垂向与水平扩散并存的二维扩散模式。
前述研究多集中于采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带含水率变化影响研究,对包气带水分运移速度及方向等变化缺少关注,同时考虑包气带水分运移规律影响因素较为单一,缺乏对多种因素下包气带水分运移规律的综合评估。为此,在综合考虑采煤塌陷裂缝宽度、密度及土壤质地类型等主控因素对包气带水分运移影响规律的基础上,利用HYDRUS 2D数值软件,开展不同主控因素条件下采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移规律影响的研究,综合分析采煤塌陷裂缝对其周边含水率、水分运移方向及运移速度的影响规律,为西北生态脆弱区采煤塌陷区的生态恢复治理提供理论支撑。
1. 采煤沉陷区包气带水分运移主控因素
土壤中的水分运移是一个复杂的过程,在这个过程中会受到多种因素的影响,如:裂缝、降水量、植被、地下水埋深、土壤质地类型等。
1.1 裂缝条件
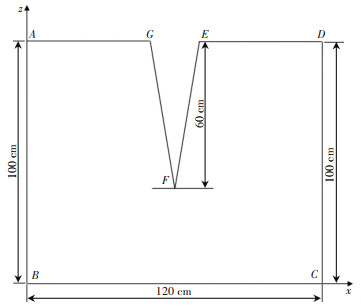
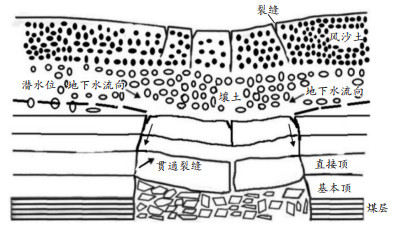
裂缝是地下水文系统中的重要水文地质结构,其对地下水的运移和储存具有重要的影响 [ 8- 9] 。采煤沉陷产生大量的沉陷裂缝,影响着包气带的水分运移。采煤塌陷区包气带结构如 图 1所示。
![]() 图 1 采煤塌陷区包气带结构 [ 10]
图 1 采煤塌陷区包气带结构 [ 10]塌陷裂缝条件包括裂缝密度、长度、宽度、连通性等因素,这些因素会影响包气带水分运移的速度、方向和规律,其中裂缝宽度对周边的水分运移影响较大 [ 6] 。裂缝是水分渗透的主要通道,当裂缝宽度较小时,水分只能通过分子扩散进入裂缝中,这种扩散的速度非常缓慢;当裂缝宽度增大时,水分的运移速度也随之增快。此外,裂缝宽度的变化对水分的储存也有重要的影响。当裂缝宽度较小时,裂缝内的水分往往无法充分储存,导致包气带中的水分储存量降低。裂缝密度的变化对周边水分变化也有较为显著的影响,裂缝是水分渗透的重要通道,裂缝密度的变化能直观地影响水分运移的速度和方向。基于此,选取采煤塌陷裂缝宽度和密度作为采煤沉陷区包气带水分运移主控因素之一。
1.2 降水量
降水影响着包气带的水分运移,降水后上层土壤的含水率增高,上下层含水率差距较大,水分向下运输加快。但这与降水的强度、时间有着很大的关系,有极大的不确定性。西北干旱地区的降水量少、蒸发量大,且降水期集中于9—10月份,大部分时间土壤水分运移系统中不存在降水影响,相较于采煤塌陷裂缝的影响,降水量对包气带水分的影响次之。
1.3 植被生态
植被对包气带的水分运移产生多种多样的影响。植被可以通过根系对包气带的水分运移起到调节作用,也可以通过覆盖地表来影响包气带的水分输入进而影响包气带的水分运输 [ 11] 。但西北干旱区域的植被覆盖较少,且采煤塌陷使原本脆弱的植被生态更加恶化。
1.4 地下水埋深
地下水的埋深会影响包气带的厚度,包气带厚度随着地下水位埋深的增大而增大 [ 12] 。张光辉等 [ 13] 对不同深度包气带的土壤含水率及水势变化进行研究,发现当包气带厚度小于潜水蒸发极限深度时,入渗速率和总入渗补给量随着包气带厚度的增加而减小,蒸发不仅消耗了地下水量,还消耗了包气带水量;当地下水位埋深较大时,蒸发消耗的包气带水量增加。所以地下水埋深在影响包气带厚度的同时也间接影响了包气带水分的蒸发和分布。
1.5 土壤质地类型
影响包气带水分运移最重要的因素就是孔隙结构,孔隙结构的差异决定了包气带储容、滞留及传输水的能力。而不同的土壤质地类型决定了不同的土壤孔隙类型,因此在研究包气带的水分运移规律时,土壤质地类型是采煤沉陷区包气带水分运移主控因素之一 [ 12] 。考虑西北干旱地区大多地处沙漠边缘,地表覆盖着风积沙,其下分布着风沙土和壤土,因此选择壤土和风沙土这2种土壤质地类型作为本研究的主控因素。
上述因素均对包气带的水分运移规律具有一定影响,但考虑到西北生态脆弱区气候、地质条件,选取采煤塌陷裂缝宽度、裂缝密度及土壤质地类型(风沙土和壤土)作为采煤沉陷区包气带水分运移主控因素。
2. 采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移的影响数值模拟方案
2.1 数值模型建立
2.1.1 土壤水分运动基本方程
假设土壤为均质、各向同性的多孔介质,且不考虑气体及温度对水分运动的影响 [ 14- 16] ,因此选用的是理查德方程(Richard’s equation) [ 17] ,其可以用来描述水分在非饱和土壤中的流动。理查德方程表达式如下:
∂θ/∂t=∇⋅(K(h)⋅∇θ)+q (1) 式中: θ为土壤体积含水率,cm 3/cm 3; t为时间,d; K( h)为土壤的渗透系数; h为土壤水头,cm; q为源项,表示降水、蒸散发等的水分输入输出。
2.1.2 土壤水分特征方程
采用Van Genuchten提出的VG模型 [ 18] 来描述土壤水分特征,其表达式如下:
K(θ)=Ksθle[1−(1−θ1me)m]2 (2) θe=θ(h)−θr(θs−θr)=(1+|ah|n)(−m) (3) 式中: K s为土壤饱和水导水率,cm/d; θ e为土壤相对饱和度,cm 3/cm 3; θ r为土壤剩余体积含水率,cm 3/cm 3; θ s为土壤饱和体积含水率,cm 3/cm 3; a、 n为由试验测定的经验函数; m=1-1/ n; h为负压水头,cm; l为经验拟合参数,通常取0.5 [ 19] 。
2.1.3 水力模型参数设置
本模拟相关水力模型参数见 表 1。
表 1 风沙土、壤土土壤水力特性参数土壤类型 θ r/(cm 3·cm -3) θ s/(cm 3·cm -3) a n K s/(cm·d -1) l 风沙土 0.036 3 0.389 8 0.044 9 1.799 6 59.60 0.5 壤土 0.078 0 0.430 0 0.036 0 1.560 0 24.96 0.5 2.1.4 模型初始条件
为了给予足够的时间使水分运移接近平衡,本次模拟选择15 d的模拟时长。时间单位为d,初始时间为0.01,最小时间步长0.001。采用二维模拟,设置的模拟区域为 x=120 cm, z=100 cm的长方形区域,如 图 2所示。
裂缝深度60 cm。计算区域中 AB及 CD选用无通量边界, BC选用自由边界, AG、 DE、 GF、 EF选用大气边界。
2.2 实验方案设计
综合考虑裂缝宽度、裂缝密度、风沙土和壤土,设计110组模拟实验方案,如 表 2所示。模拟中土壤叠层时,选择上层为风沙土、下层为壤土的组合。
表 2 数值模拟试验工况土壤质地类型 裂缝条数 裂缝宽度/cm 单层壤土 1 每组工况均开展10个裂缝宽度:2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20 单层风沙土 1 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 1 双层土壤(上层40 cm、下层60 cm) 1 双层土壤(上层50 cm、下层50 cm) 1 单层壤土 2 单层风沙土 2 单层壤土 3 单层风沙土 3 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 2 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 3 3. 采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移规律影响模拟结果与分析
3.1 裂缝对周边土壤含水率的影响分析
1) 单裂缝时,在土壤深度30 cm处设立观测点,土壤初始含水率均为0.250 0 cm 3/cm 3,收集第15天的数据进行分析。裂缝宽度为20 cm时,距离裂缝0、25、50 cm处的土壤含水率为0.160 6、0.162 4、0.163 1 cm 3/cm 3。裂缝宽度为2、10、20 cm时,风沙土裂缝边缘处的含水率分别为0.163 7、0.162 1、0.160 6 cm 3/cm 3。数据表明,远离裂缝的区域的含水率明显高于靠近裂缝的区域,这个含水率差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系。且在整个模拟过程中,含水率一直保持这个规律。
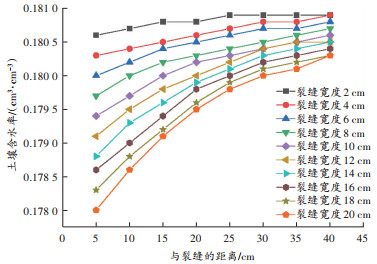
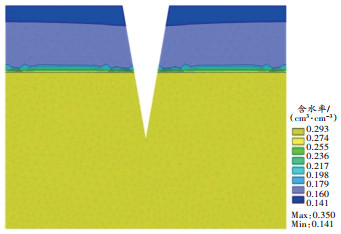
为了能直观地看到含水率的差距,选择已经模拟了一段时间的结果来展示,即选择第7.5天。单裂缝条件下风沙土不同宽度裂缝数值模拟第7.5天包气带含水率如 图 3所示。
当裂缝宽度为2 cm时,距离裂缝25~40 cm区域的含水率基本保持一致,含水率降低区域的边界距裂缝25 cm;当裂缝宽度为20 cm时,该区域的含水率受裂缝影响产生了差异,含水率降低区域的边界距裂缝40 cm;表明受到裂缝影响使得含水率降低的区域也会随着裂缝宽度的增大而增大。这个结果与许传阳等 [ 20] 的研究结果一致。
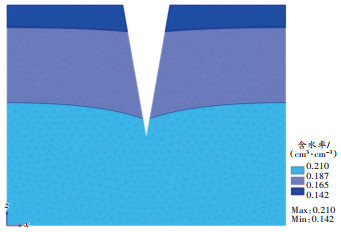
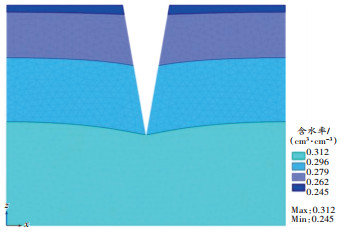
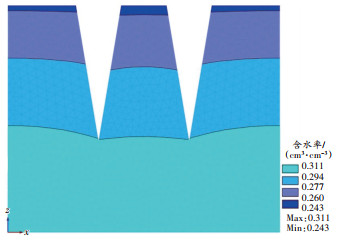
单裂缝裂缝宽度20 cm壤土和风沙土模拟结果如 图 4、 图 5所示。
模拟设置的裂缝深度为60 cm。 图 4中60 cm深度处风沙土的最低含水率为0.191 5 cm 3/cm 3, 图 5中60 cm深度处壤土的最低含水率为0.295 4 cm 3/cm 3,表明其他条件相同时,壤土的含水率高于风沙土的含水率。
单裂缝双层土壤裂缝宽度为20 cm时的模拟结果如 图 6所示。
从 图 6中可以看出,裂缝周边土壤含水率,仍然呈现在同一土壤深度时,靠近裂缝的区域的土壤含水率低于远离裂缝的区域,含水率差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系。但在2种土壤交界处有水分聚集现象,交界面处含水率变化速度明显慢于土壤内部,上层风沙土对比其他条件相同时的风沙土模拟结果含水率基本一致,但下层的壤土对比其他条件相同时的壤土模拟结果含水率明显较低。
2) 双裂缝时,在土壤深度30 cm处设立观测点,土壤初始含水率均为0.250 0 cm 3/cm 3,收集第15天的数据进行分析。裂缝宽度20 cm时,在一侧有裂缝的区域中,距离裂缝0、15、30 cm处的含水率分别为0.160 2、0.161 6、0.162 0 cm 3/cm 3,被裂缝包夹区域距离裂缝0 cm处的含水率为0.158 3 cm 3/cm 3。裂缝宽度为2、10、20 cm时,风沙土裂缝边缘处的含水率分别为0.163 4、0.162 0、0.160 2 cm 3/cm 3。双裂缝裂缝宽度为20 cm时的数值模拟含水率图如 图 7所示。
结合 图 7与前文数据表明,裂缝周边靠近裂缝区域的土壤含水率仍低于远离裂缝的区域,含水率差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离均呈正相关关系。且裂缝密度增高,土壤的含水率降低,这与张延旭等 [ 6] 的研究结果相近。多条裂缝之间的区域的土壤含水率低于一侧有裂缝的区域。裂缝密度增高、其他条件相同时,对比壤土、风沙土、叠层土壤的模拟结果后,仍呈现同一土壤深度壤土的含水率高于风沙土的含水率,叠层土壤交界面上水分堆积,交界面上方风沙土的含水率与同一土壤深度的单一风沙土模拟结果几乎一致,交界面下方的壤土含水率低于同一深度单一壤土模拟结果。
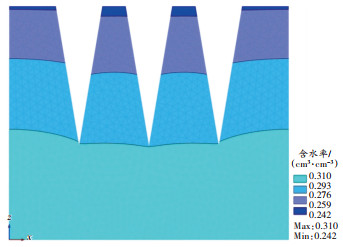
3) 三裂缝时,在土壤深度30 cm处设立观测点,土壤初始含水率均为0.250 0 cm 3/cm 3,收集第15天的数据进行分析。裂缝宽度为20 cm时,一侧有裂缝区域中距离裂缝0、10、20 cm处的含水率分别为0.159 4、0.160 4、0.160 9 cm 3/cm 3,被裂缝包夹的区域中距离裂缝0 cm处的含水率为0.156 5 cm 3/cm 3。裂缝宽度为2、10、20 cm时,风沙土裂缝边缘的含水率分别为0.163 4、0.161 7、0.159 4 cm 3/cm 3。三裂缝裂缝宽度20 cm时的数值模拟含水率如 图 8所示。
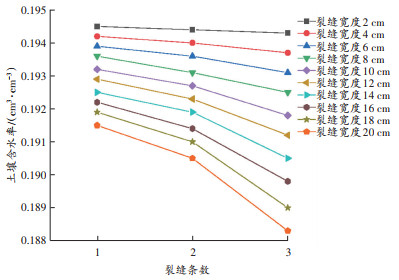
结合 图 8与前文数据表明,裂缝密度进一步增高后,仍呈现靠近裂缝区域的土壤含水率低于远离裂缝的区域,含水率差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系。多条裂缝之间的区域的含水率低于一侧有裂缝区域的含水率。不同裂缝密度和裂缝宽度的60 cm深处土壤最低含水率如 9图所示。
结合 图 9和前文的分析表明,随着裂缝密度不断增高,土壤的含水率随之降低。在三裂缝的条件下再对比壤土、风沙土、叠层土壤的模拟结果,仍呈现同一土壤深度壤土的含水率高于风沙土含水率,叠层土壤交界面上水分堆积,使得堆积区域上方风沙土的含水率与同一土壤深度的单一风沙土含水率模拟结果几乎一致,堆积区域下方的壤土含水率低于同一深度单一壤土含水率模拟结果。
3.2 裂缝对周边水分运移方向的影响分析
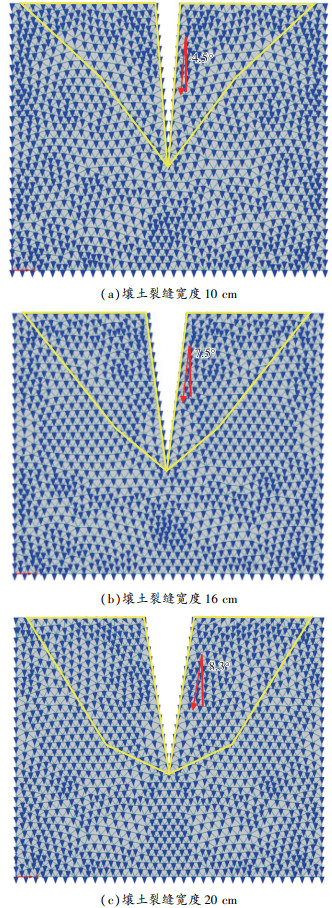
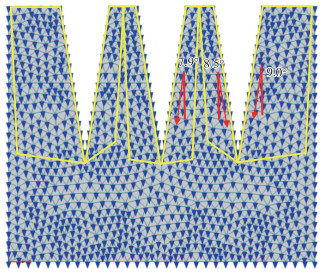
1) 单裂缝壤土条件下,不同宽度(10、16、20 cm)裂缝数值模拟水分运移方向部分结果如 图 10所示。
裂缝宽度为10、16、20 cm时,裂缝边缘的水分运移方向最大偏转角分别为4.5°、7.5°、8.3°。 图 10中黄色线条框出的区域表示发生水分运移方向偏转的区域。结果表明,在裂缝边缘的水分运移方向发生明显偏转,距离裂缝越远的区域偏转角度越小,直至不受影响。且发生运移角度偏转的区域大小和最大偏转角度与裂缝宽度呈正相关关系。
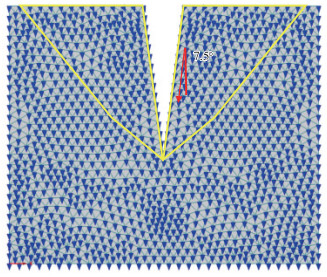
其他条件相同的情况下,壤土和风沙土水分运移方向模拟结果如 图 10(b)、 图 11所示。
对比结果表明,2种土壤在裂缝边缘处的水分运移方向偏转角度一致,发生土壤水分运移方向偏转的区域基本相同,土壤条件对土壤水分运移方向偏转几乎没有影响。
单裂缝叠层土壤的模拟结果如 图 12所示。
由 图 12可见,在土壤分界面上下的水分运移方向仍一致,土壤类型对土壤水分运移方向偏转几乎没有影响。
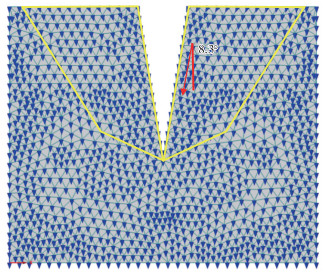
2) 双裂缝,宽度为20 cm时,包气带水分运移方向数值模拟结果如 图 13所示。
由 图 13可见,一侧有裂缝区域的最大偏转角度为9.0°,裂缝包夹的区域的最大偏转角度为8.5°。 图 13中黄线框出区域表示发生偏转的区域,表明在2条裂缝之间的区域由于两侧裂缝的复合作用,其水分运移方向偏转最大角度及发生偏转的区域相比于一侧有裂缝的区域均相对较小。
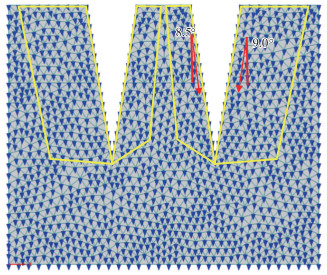
3) 三裂缝,宽度为20 cm时,水分运移方向数值模拟结果如 图 14所示。
由 图 14可见,一侧有裂缝区域的最大偏转角度为9.0°,裂缝包夹的区域中,远离中心一侧的最大偏转角度为8.5°,靠近中心一侧的最大偏转角度为7.9°。 图 14中黄线框出的区域表示发生偏转的区域,表明裂缝密度增高后,受到更多裂缝共同影响的区域的最大偏转角度会越小,发生偏转的区域会变小。
3.3 裂缝对周边水分运移速度的影响分析
水分的平均运移速度为流量除以时间,即含水率的变化反映了平均水分运移速度的变化。据此,在裂缝对含水率影响的基础上,分析裂缝对周边水分运移速度的影响。
单裂缝时,裂缝边缘的平均流速均高于远离裂缝区域,且平均水分运移速度的差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系。
双裂缝和三裂缝时,仍是裂缝边缘的平均流速均高于远离裂缝区域,且平均水分运移速度差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系。但同一土壤深度,裂缝之间的区域的水分运移速度高于一侧有裂缝区域。
在任何裂缝条件下,单一壤土同一位置的水分运移速度低于风沙土。土壤叠层时,上层水分运移速度与单一风沙土基本一致,但下层壤土的水分运移速度明显高于单一壤土条件时的运移速度。
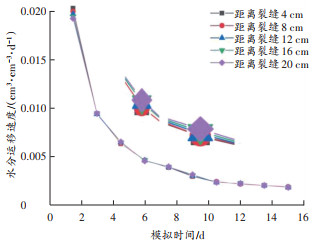
为探究模拟过程中不同区域瞬时流速的变化,裂缝宽度为16 cm时壤土水分运移瞬时速度与时间的关系如 图 15所示。
由 图 15可见,在整个过程中不同区域的瞬时流速的大小因为周边含水率等因素变化的影响是不定的。
4. 结论
1) 在单一裂缝时,同一土壤深度靠近裂缝的区域的土壤含水率低于远离裂缝的区域,且含水率差与裂缝宽度,以及与裂缝的距离呈正相关关系,含水率降低的区域大小随裂缝宽度的变大而变大。
在裂缝密度增高时,同一土壤深度的含水率随裂缝数量的增多而降低,裂缝之间区域的含水率低于一侧有裂缝区域的含水率。
在其他条件相同的情况下,同一土壤深度下壤土的含水率明显高于风沙土含水率。在2种土壤叠层的情况下,在土壤交界处上方出现水分聚集现象,上方风沙土区域含水率与单一风沙土含水率模拟结果基本相同,下方壤土区域含水率低于相同初始条件的单一壤土的含水率。
2) 单一裂缝时,在同一土壤深度时,整个区域的土壤水分运移方向向裂缝处发生偏转,越靠近裂缝的区域偏转角度越大,且最大偏转角度和发生水分运移方向变化的区域大小随裂缝宽度变大而变大。土壤条件对水分运移方向变化几乎没有影响。
裂缝密度增高后,由于两侧裂缝的复合作用,裂缝之间的区域相对于一侧有裂缝的区域,水分运移方向偏转最大角度变小,发生偏转的区域变小。
3) 单一裂缝时,同一土壤深度靠近裂缝的区域整个模拟过程中的平均水分运移速率高于远离裂缝的区域,同一土壤深度裂缝边缘的平均水分运移速度随裂缝宽度的增大而增大。且其他条件相同时风沙土条件的平均水分运移速度高于壤土条件的水分运移速度。裂缝密度增高后,在与裂缝距离相同时,一侧有裂缝区域的水分运移速度要低于裂缝之间区域的运移速度。在整个过程中不同区域瞬时流速的高低因为周边含水率等因素的影响是不定的。
-
图 1 采煤塌陷区包气带结构 [ 10]
表 1 风沙土、壤土土壤水力特性参数
土壤类型 θ r/(cm 3·cm -3) θ s/(cm 3·cm -3) a n K s/(cm·d -1) l 风沙土 0.036 3 0.389 8 0.044 9 1.799 6 59.60 0.5 壤土 0.078 0 0.430 0 0.036 0 1.560 0 24.96 0.5 表 2 数值模拟试验工况
土壤质地类型 裂缝条数 裂缝宽度/cm 单层壤土 1 每组工况均开展10个裂缝宽度:2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20 单层风沙土 1 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 1 双层土壤(上层40 cm、下层60 cm) 1 双层土壤(上层50 cm、下层50 cm) 1 单层壤土 2 单层风沙土 2 单层壤土 3 单层风沙土 3 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 2 双层土壤(上层30 cm、下层70 cm) 3 -
[1] 李晓斌, 李全生, 韩鹏华, 等. 高强度开采地表损伤程度分类判别与控制研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2022, 4(3): 90-99. [2] 李文平, 王启庆, 刘士亮, 等. 生态脆弱区保水采煤矿井(区)等级类型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(3): 718-726. [3] 琚成远, 浮耀坤, 陈超, 等. 神南矿区采煤沉陷裂缝对土壤表层含水量的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(4): 309-316. [4] 毕银丽, 伍越, 张健, 等. 采用HYDRUS模拟采煤沉陷地裂缝区土壤水盐运移规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(1): 360-367. [5] 杜国强, 陈秀琴, 郄晨龙, 等. 半干旱矿区地裂缝对土壤水分和地表剪切强度的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2016, 32(2): 224-228. [6] 张延旭, 毕银丽, 陈书琳, 等. 半干旱风沙区采煤后裂缝发育对土壤水分的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(3): 11-14. [7] 陈建平, 朱哲, 吴丽. 基于塌陷裂缝非连续均质的土壤水分扩散物理模拟[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(2): 66-72. [8] 尚京萱, 陈实, 刘骞文, 等. 采煤塌陷裂缝对沙蒿吸水来源影响试验研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(12): 96-104. [9] BEVEN K, GERMANN P. Macropores and water flow in soils[J]. Water Resour Res, 1982, 18(5): 1311-1325. doi: 10.1029/WR018i005p01311
[10] 张发旺, 宋亚新, 赵红梅, 等. 神府—东胜矿区采煤塌陷对包气带结构的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(1): 178-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.01.027 [11] 赵贵章. 鄂尔多斯盆地风沙滩地区包气带水—地下水转化机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2011. [12] 徐远志, 赵贵章, 母霓莎, 等. 包气带水分运移过程的影响因素综述[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(2): 37-41. [13] 张光辉, 费宇红, 申建梅, 等. 降水补给地下水过程中包气带变化对入渗的影响[J]. 水利学报, 2007, 38(5): 611-617. [14] 赵丽. 中宁平原包气带水分运移对地下水补给和蒸发的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. [15] 崔赫钊, 周青云, 韩娜娜, 等. 基于HYDRUS-2D模型的滴灌土壤水氮动态模拟研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2023, 42(4): 57-66. [16] 李鑫, 孙亚军, 陈歌, 等. 高矿化度矿井水深部转移存储介质条件及影响机制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(5): 17-28. [17] KANDELOUS M M, ŠIMŮNEK J, VAN GEUNCHTEN M T, et al. Soil water content distributions between two emitters of a subsurface drip irrigation system[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2011, 75(2): 488-497.
[18] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898.
[19] 李亮, 史海滨, 贾锦凤, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区荒地水盐运移规律模拟[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(1): 31-35. [20] 许传阳, 马守臣, 张合兵, 等. 煤矿沉陷区沉陷裂缝对土壤特性和作物生长的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(5): 597-604. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 龙晓峰,贺勇,张召,陈科平,金福喜,魏贺,张可能. 普朗铜矿区土壤水分运移动态监测与数值模拟研究. 矿产勘查. 2024(08): 1500-1507 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: